What Is The Skin Under Fingernails
| Nail | |
|---|---|
 | |
 A gorilla's fingernails | |
| Details | |
| System | Integumentary organisation |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | unguis |
| MeSH | D009262 |
| TA98 | A16.0.01.001 |
| TA2 | 7065 |
| Thursday | H3.12.00.iii.02001 |
| FMA | 54326 |
| Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] | |
A nail is a hook-like plate at the tip of the fingers and toes in most primates. Nails correspond to claws establish in other animals. Fingernails and toenails are made of a tough protective protein called blastoff-keratin, which is a polymer. Blastoff-keratin is establish in the hooves, claws and horns of vertebrates.[1]
Structure [edit]
Fingernails

Toenails
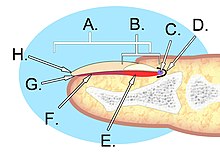
A. Boom plate; B. lunula; C. root; D. sinus; E. matrix; F. blast bed; G. hyponychium; H. free margin.
The nail consists of the smash plate, the smash matrix and the nail bed below it, and the grooves surrounding information technology.[2]
Parts of the nail [edit]
The matrix, sometimes called[3] the matrix unguis, keratogenous membrane, nail matrix, or onychostroma, is the active tissue (or germinal matrix) that generates cells, which harden as they motion outward from the boom root to the smash plate.[iv] It is the role of the nail bed that is beneath the smash and contains nerves, lymph and blood vessels.[5] The matrix produces cells that become the nail plate. The width and thickness of the nail plate is determined by the size, length, and thickness of the matrix, while the shape of the fingertip bone determines if the nail plate is flat, arched, or hooked.[6] The matrix will continue to produce cells as long as it receives nutrition and remains in a healthy condition.[7] As new smash plate cells are made, they push older blast plate cells frontwards; and in this style older cells become compressed, apartment, and translucent. This makes the capillaries in the nail bed below visible, resulting in a pink color.[ citation needed ]
The lunula ("small moon") is the visible part of the matrix, the whitish crescent-shaped base of the visible nail.[ citation needed ] The lunula tin best be seen in the thumb and may not be visible in the pinkie. The lunula appears white due to a reflection of light at the betoken where the nail matrix and nail bed meet.
The nail bed is the skin below the nail plate.[ citation needed ] It is the area of the smash on which the nail plate rests. Nerves and blood vessels found here supply nourishment to the entire nail unit. Like all skin, it is made of two types of tissues: the dermis and the epidermis. The epidermis is attached to the dermis past tiny longitudinal "grooves" called matrix crests (cristae matricis unguis).[4] In onetime age, the nail plate becomes thinner, and these grooves become more than visible.[ citation needed ] The boom bed is highly innervated, and removal of the blast plate is oftentimes excruciatingly painful as a result.
The nail sinus (sinus unguis) is where the boom root is;[4] i.eastward. the base of the nail underneath the skin. It originates from the actively growing tissue below, the matrix.[ commendation needed ]
The nail plate (corpus unguis)[4] sometimes referred to as the blast body, is the visible hard nail area from the nail root to the free border, made of translucent keratin protein. Several layers of dead, compacted cells crusade the nail to exist strong only flexible. Its (transverse) shape is determined past the form of the underlying bone.[ citation needed ] In mutual usage, the word smash often refers to this part merely. The nail plate is strongly attached to the nail bed and does not contain whatsoever nerves or claret vessels.
The free margin (margo liber) or distal border is the anterior margin of the boom plate corresponds to the abrasive or cutting edge of the smash.[4] The hyponychium (informally known as the "quick")[eight] is the epithelium located below the nail plate at the junction between the free edge and the skin of the fingertip. Information technology forms a seal that protects the smash bed. The onychodermal band is the seal betwixt the nail plate and the hyponychium. It is just under the free edge, in that portion of the nail where the nail bed ends and can be recognized in fair-skinned people by its glassy, greyish colour. It is not visible in some individuals while it is highly prominent on others.[ citation needed ]
Eponychium [edit]
Together, the eponychium and the cuticle form a protective seal. The cuticle is the semi-circular layer of nigh invisible dead skin cells that "ride out on" and cover the back of the visible nail plate while the eponychium is the fold of peel cells that produces the cuticle. They are continuous, and some references view them equally 1 entity; in this classification, the names eponychium, cuticle, and perionychium are synonymous.[nine] It is the cuticle (nonliving part) that is removed during a manicure, but the eponychium (living part) should non be touched due to risk of infection.[ citation needed ] The eponychium is a small band of living cells (epithelium) that extends from the posterior nail wall onto the base of the nail.[4] The eponychium is the end of the proximal fold that folds back upon itself to shed an epidermal layer of pare onto the newly formed nail plate.[ contradictory ] The perionyx is the projecting edge of the eponychium covering the proximal strip of the lunula.[four]
The boom wall (vallum unguis) is the cutaneous fold overlapping the sides and proximal end of the boom. The lateral margin (margo lateralis) lies beneath the smash wall on the sides of the nail, and the blast groove or fold (sulcus matricis unguis) are the cutaneous slits into which the lateral margins are embedded.[iv]
Paronychium [edit]
The paronychium is the soft tissue edge effectually the nail,[10] and paronychia is an infection in this area. The paronychium is the pare that overlaps onto the sides of the nail plate, also known as the paronychial edge. The paronychium is the site of hangnails, ingrown nails, and paronychia, a pare infection.
Hyponychium [edit]
The hyponychium is the area of epithelium, particularly the thickened portion, underlying the costless border of the nail plate. It is sometimes chosen the "quick", every bit in the phrase "cutting to the quick".
Part [edit]
A salubrious fingernail has the function of protecting the distal phalanx, the fingertip, and the surrounding soft tissues from injuries. Information technology also serves to heighten precise delicate movements of the distal digits through counter-pressure exerted on the pulp of the finger.[2] The blast then acts every bit a counter-force when the end of the finger touches an object, thereby enhancing the sensitivity of the fingertip,[11] although the nail itself has no nerve endings. Finally, the nail functions equally a tool enabling a so-chosen "extended precision grip" (e.g., pulling out a splinter in 1's finger), and certain cutting or scraping actions.
Growth [edit]
The growing function of the smash is under the peel at the nail'south proximal end under the epidermis, which is the only living office of a boom.
In mammals, the growth charge per unit of nails is related to the length of the terminal phalanges (outermost finger bones). Thus, in humans, the blast of the alphabetize finger grows faster than that of the little finger; and fingernails grow upwardly to iv times faster than toenails.[12]
In humans, fingernails grow at an boilerplate rate of approx. 3.5 mm (0.fourteen in) a calendar month, whereas toenails grow about half as chop-chop (approx. average 1.6 mm (0.063 in) a month).[13] Fingernails require three to vi months to regrow completely, and toenails require twelve to xviii months. Actual growth rate is dependent upon age, sex activity, flavor, exercise level, nutrition, and hereditary factors.[14] The longest female nails known ever to have existed measured a total of viii.65 k (28 ft 4.5 in).[15] Contrary to popular belief, nails do not go on to abound afterwards death; the peel dehydrates and tightens, making the nails (and hair) appear to abound.[16]
Permeability [edit]
The nail is often considered an impermeable barrier, merely this is not true. In fact, information technology is much more than permeable than the skin,[17] and the composition of the nail includes 7–12% water. This permeability has implications for penetration by harmful and medicinal substances; in particular cosmetics practical to the nails tin pose a risk. Water can penetrate the nail as tin many other substances including paraquat, a fast acting herbicide that is harmful to humans, urea which is oftentimes an ingredient in creams and lotions meant for use on hands and fingers, and several fungicidal agents such as salicylic acid, miconazole branded Monistat, natamycin; and sodium hypochlorite which is the active ingredient in common household bleach (just unremarkably only in two–3% concentration).[17]
Clinical significance [edit]

Healthcare and pre-hospital-intendance providers (EMTs or paramedics) often use the fingernail beds as a brief indicator of distal tissue perfusion of individuals who may be dehydrated or in daze.[18] However, this test is non considered reliable in adults.[19] This is known as the CRT or flinch examination. The fingernail bed is briefly depressed to plough the boom-bed white. When the pressure is released, the normal pink colour should exist restored within a second or 2. Delayed return to pinkish colour can be an indicator of certain daze states such equally hypovolemia.[20] [21]
Nail growth record can show the history of recent health and physiological imbalances, and has been used equally a diagnostic tool since ancient times.[22] Deep, horizontally transverse grooves known as "Beau's lines" may form across the nails (horizontal, not along the smash from cuticle to tip). These lines are usually a natural consequence of aging, although they may result from affliction. Discoloration, thinning, thickening, brittleness, splitting, grooves, Mees' lines, small white spots, receded lunula, clubbing (convex), flatness, and spooning (concave) tin can signal illness in other areas of the trunk, nutrient deficiencies, drug reaction or poisoning, or merely local injury.
Nails can also become thickened (onychogryphosis), loosened (onycholysis), infected with fungus (onychomycosis), or degenerate (onychodystrophy). A common blast disorder is an ingrowing toenail (onychocryptosis).
Dna profiling is a technique employed past forensic scientists on pilus, fingernails, toenails, etc.
Health and care [edit]

A set of professional nail care tools
The best way to care for nails is to trim them regularly. Filing is besides recommended, as to keep nails from becoming also rough and to remove any minor bumps or ridges that may cause the nail to get tangled up in materials such as material.[23]
Bluish or purple fingernail beds may exist a symptom of peripheral cyanosis, which indicates oxygen deprivation.
Nails can dry out out, simply like skin. They can as well pare, break, and be infected. Toe infections, for instance, can be caused or exacerbated by dirty socks, specific types of aggressive exercise (long-altitude running), tight footwear, and walking unprotected in an unclean environment.[ citation needed ] Mutual organisms causing nail infections include yeasts and molds (particularly dermatophytes).[24]
Smash tools used past different people may transmit infections. Standard hygiene and sanitation procedures avoid manual. In some cases, gel and foam cuticle removers can be used instead of cuticle scissors.
Boom disease can be very subtle and should be evaluated past a dermatologist with a focus in this detail expanse of medicine. Nevertheless, near times it is a nail technician who volition notation a subtle change in boom illness.
Inherited accessory nail of the fifth toe occurs where the toenail of the smallest toe is separated, forming a smaller "6th toenail" in the outer corner of the boom.[25] Like whatever other boom, information technology tin can be cutting using a nail clipper.
Effect of nutrition [edit]
Biotin-rich foods[26] and supplements may help strengthen brittle fingernails. A few small studies support biotin supplement utilize to that effect.[27] 1 study in 35 people with breakable fingernails found that two.v mg of biotin per day for six weeks to seven months improved symptoms in 63% of participants.[28]
Vitamin A is an essential micro-nutrient for vision, reproduction, cell and tissue differentiation, and immune role. Vitamin D and calcium piece of work together in cases of maintaining homeostasis, creating musculus contraction, manual of nerve pulses, blood clotting, and membrane structure. A lack of vitamin A, vitamin D, or calcium tin can cause dryness and brittleness.
Insufficient vitamin B12 can lead to excessive dryness, darkened nails, and rounded or curved nail ends. Bereft intake of both vitamin A and B results in delicate nails with horizontal and vertical ridges. Some over-the-counter vitamin supplements such as certain multivitamins and biotin may help in growth of strong nails, although this is quite subjective. Both vitamin B12 and folate play a part in red blood cell product and oxygen transportation to boom cells. Inadequacies tin can upshot in discoloration of your nails.[29]
Omega-three fatty acids[xxx] can help lubricate and moisturize your nails, giving them a shiny appearance. These fatty acids may also reduce inflammation in your nail bed, which nourishes and promotes the health of cells that give ascent to your boom plate. A lack of omega-3 fatty acids could contribute to dry and brittle nails.[31] [32]
Poly peptide is a building material for new nails; therefore, low dietary protein intake may crusade anemia and the resultant reduced hemoglobin in the blood filling the capillaries of the nail bed reflects varying amounts of calorie-free incident on the blast matrix resulting in lighter shades of pinkish ultimately resulting in white nail beds when the hemoglobin is very low. When hemoglobin is shut to 15 or 16 grams, nigh of the spectrum of lite is absorbed and only the pink color is reflected back and the nails await pink.
Essential fatty acids play a big role in salubrious peel equally well as nails. Splitting and flaking of nails may be due to a lack of linoleic acid.
Iron-deficiency anemia[33] tin lead to a pale colour forth with a thin, brittle, ridged texture. Iron deficiency in general may crusade the nails to become flat or concave, rather than convex. As oxygen is needed for healthy nails, an fe deficiency or anemia tin can lead to vertical ridges in your nails or your nails may concave or "spoon".[34] RDAs for iron vary considerably depending on age and gender. The recommendation for men is eight mg per day, while that of women aged xix–l is xviii mg per day. After women striking age 50 or become through menopause, their fe needs drop to 8 mg daily.[35] [36]
Social club and culture [edit]
Manner [edit]

Manicures (for the hands) and pedicures (for the feet) are health and cosmetic procedures to groom, trim, and paint the nails and manage calluses. They require diverse tools such as cuticle scissors, nail pair of scissors, nail clippers, and boom files. Artificial nails tin likewise be fixed onto real nails for cosmetic purposes.
A person whose occupation is to cutting, shape and intendance for nails also every bit to apply overlays such as acrylic and UV gel is sometimes called a nail technician. The place where a nail technician works may exist a nail salon or nail store or nail bar.

Acrylic nails are made out of acrylic drinking glass (PMMA). When it is mixed with a liquid monomer (usually ethyl methacrylate mixed with some inhibitor) it forms a malleable bead. This mixture begins to cure immediately, continuing until completely solid in minutes. Acrylic nails can final upward to 21 days but tin can terminal longer with touch-ups. To give acrylic nails color, gel polish, nail polish, and dip powders can exist applied.[37]
Painting the nails with colored nail polish (also chosen nail lacquer and nail varnish) to improve the advent is a common practice dating back to at least 3000 B.C. With the rise of smartphones, some analysts have noted a trend of the nelfie (nail selfie), wherein people share their nail art online.[38] Gel blast extensions and gel smash shine. Below are diverse manicure tools including a UV lamp for curing gel nails. Gel nails can be utilized in guild to create artificial nail extensions, but can too exist used like nail shine. They are hardened using ultraviolet low-cal. They last longer than regular nail polish and do not chip. They have a high-gloss finish and last for 2 to three weeks.[39]
Nail wraps are formed by cut pieces of fiberglass,[40] [ round reference ] linen, silk material, or some other material to fit on the surface of the smash (or a tip attached prior), to be sealed onto the nail plate with a layer of resin or glue. They do not damage the smash and also provide forcefulness to the nail but are not used to lengthen it. It can as well be used to set cleaved nails. The treatment is however more expensive.
With the dip powder method, a clear liquid is brushed onto a nail and the nail is so placed into pigmented powder.[41] Dip nails tend to last nigh a month, 2-3 weeks longer than gel and acrylic nails. It can be worn on natural nails, or with tips to create an artificial nail. Dip powder nails exercise non require any UV/LED light to be cured, instead they are sealed using an activator.[ commendation needed ] The quickest way to remove dip pulverization is to drill, clip off, or buff out layers of the powder and so, when they are soaking in acetone, they slide correct off.[42] [43]
Length records [edit]
Guinness World Records began tracking record fingernail lengths in 1955, when a Chinese priest was listed every bit having fingernails one foot 10.75 inches (57.79 cm) long.
The current record-holder for men, according to Guinness, is Shridhar Chillal from India who fix the record in 1998 with a total of twenty feet 2.25 inches (615.32 cm) of nails on his left hand. His longest nail, on his thumb, was 4 anxiety ix.6 inches (146.3 cm) long.
The tape-holder for women is Lee Redmond of the U.S., who fix the record in 2001 and every bit of 2008 had nails with a total length on both hands of 28 anxiety (850 cm), with the longest nail on her right thumb at ii feet 11 inches (89 cm).[44]
Evolution in primates [edit]

The smash is an unguis, significant a keratin construction at the stop of a digit. Other examples of ungues include the hook, hoof, and talon. The nails of primates and the hooves of running mammals evolved from the claws of before animals.[45]
In contrast to nails, claws are typically curved ventrally (downward in animals) and compressed sideways. They serve a multitude of functions—including climbing, digging, and fighting—and have undergone numerous adaptive changes in unlike animal taxa. Claws are pointed at their ends and are composed of two layers: a thick, deep layer and a superficial, hardened layer which serves a protective office. The underlying bone is a virtual mold of the overlying horny structure and therefore has the same shape as the claw or smash. Compared to claws, nails are flat, less curved, and do non extend far beyond the tip of the digits. The ends of the nails ordinarily consist only of the "superficial", hardened layer and are not pointed similar claws.[45]
With but a few exceptions, primates retain plesiomorphic (original, "archaic") easily with five digits, each equipped with either a nail or a claw. For example, nearly all living strepsirrhine primates take nails on all digits except the 2nd toe which is equipped with a preparation claw. Tarsiers have a grooming claw on 2d and 3rd toes. Less commonly known, a grooming claw is also found on the second pedal digit of owl monkeys (Aotus), titis (Callicebus), and peradventure other New Earth monkeys.[46] The needle-clawed bushbaby (Euoticus) has keeled nails (the thumb and the start and the second toes accept claws) featuring a central ridge that ends in a needle-similar tip.
A study of the fingertip morphology of four small-bodied New Earth monkey species indicated a correlation betwixt increasing small-co-operative foraging and:
- expanded upmost pads (fingertips),
- developed epidermal ridges (fingerprints),
- broadened distal parts of distal phalanges (fingertip basic), and
- reduced flexor and extensor tubercles (attachments areas for finger muscles on bones).
This suggests that whereas claws are useful on large-diameter branches, wide fingertips with nails and epidermal ridges were required for habitual locomotion on small-diameter branches. It also indicates keel-shaped nails of Callitrichines (a family of New World monkeys) is a derived postural adaptation rather than retained ancestral condition.[47]
Encounter also [edit]
- Listing of cutaneous conditions
- Nail disease
- Blast fetish
- Onychogryphosis, overgrown, claw-like nails
References [edit]
- ^ Wang, Bin (2016). "Keratin: Structure, mechanical properties, occurrence in biological organisms, and efforts at bioinspiration" (PDF). Progress in Materials Science. 76: 229–318. doi:ten.1016/j.pmatsci.2015.06.001.
- ^ a b Onumah, Neh; Scher, Richard Grand (May 2009). "Nail Surgery". eMedicine. Retrieved ten March 2010.
- ^ "Blast matrix". Biology Online. 2005. Retrieved 10 March 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f one thousand h Feneis, Heinz (2000). Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy (4th ed.). Thieme. pp. 392–95. ISBN3-thirteen-511204-7.
- ^ "Smash Matrix: Anatomy, Office, Injuries, and Disorders". Healthline. 2018-12-17. Retrieved 2021-09-01 .
- ^ "Nail Matrix: Anatomy, Function, Injuries, and Disorders". Healthline. 2018-12-17. Retrieved 2021-09-01 .
- ^ D. Schoon, Dougles (2005). Nail Structure and Products Chemistry. Milady. p. 6.
- ^ Crouch, James Ensign (1985). Functional human anatomy. Lea & Febiger. p. 80. ISBN9780812109306.
- ^ Elsevier, Dorland'due south Illustrated Medical Dictionary, Elsevier.
- ^ Hashemite kingdom of jordan, Christopher; Mirzabeigi, Edwin (2000-04-01). Atlas of orthopaedic surgical exposures. Thieme. p. 101. ISBN0-86577-776-4.
- ^ Wang, Quincy C; Johnson, Brett A (May 2001). "Fingertip Injuries". American Family Physician. 63 (10): 1961–half dozen. PMID 11388710. Archived from the original on 13 October 2008. Retrieved 10 March 2010.
- ^ Cartmill, Matt; Lemelin, Pierre; Schmitt, Daniel (2007). "Primate Gaits and Primate Origins". In Ravosa, Matthew J.; Dagosto, Marian (eds.). Primate Origins: Adaptations and Evolution . pp. 403–35. doi:ten.1007/978-0-387-33507-0_12. ISBN978-0-387-30335-2.
- ^ Yaemsiri, S.; Hou, North.; Slining, M. M.; He, K. (2010). "Growth rate of human fingernails and toenails in salubrious American young adults". Journal of the European University of Dermatology and Venereology. 24 (four): 420–423. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03426.x. ISSN 1468-3083. PMID 19744178. S2CID 856692.
- ^ Hunter, J. A. A., Savin, J., & Dahl, M. 5. (2002). Clinical dermatology. Malden, Mass: Blackwell Science. p. 173. ISBN 0-632-05916-viii
- ^ "A nail-biting encounter with the woman who has the longest fingernails". Guinness World Records. 2019-xi-04. Retrieved 2020-11-07.
- ^ Vreeman, R. C; Carroll, A. Eastward (2007). "Medical myths". BMJ. 335 (7633): 1288–nine. doi:ten.1136/bmj.39420.420370.25. PMC2151163. PMID 18156231.
- ^ a b K. A. Walters and G. L. Flynn, Permeability characteristics of the human nail plate, International Journal of Cosmetic Science five, 231–46 (1983)
- ^ Monterey Canton EMS Manual Archived 2008-12-16 at the Wayback Machine. Chapter XI, Patient assessment.
- ^ Schriger DL, Baraff LJ (Jun 1991). "Capillary refill – is information technology a useful predictor of hypovolemic states?". Ann Emerg Med. 20 (vi): 601–15. doi:10.1016/S0196-0644(05)82375-3. PMID 2039096.
- ^ MedlinePlus Encyclopedia: Capillary nail refill test
- ^ St. Luke's Hospital. Capillary boom refill test.
- ^ American University of Dermatology – Nail Health
- ^ Cohen, Philip R.; Scher, Richard K. (1992-04-01). "Geriatric nail disorders: Diagnosis and treatment". Journal of the American University of Dermatology. 26 (four): 521–531. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(92)70075-Q. ISSN 0190-9622. PMID 1597537.
- ^ Denning, DW; Evans, EG; Kibbler, CC; Richardson, Physician; Roberts, MM; Rogers, TR; Warnock, DW; Warren, RE (November 11, 1995). "Fungal smash illness: a guide to good practice (study of a Working Group of the British Gild for Medical Mycology)". British Medical Journal. 311 (7015): 1277–81. doi:x.1136/bmj.311.7015.1277. PMC2551187. PMID 7496239.
- ^ Haneke E (May 2016). "Double Nail of the Little Toe". Peel Appendage Disorders. ane (4): 163–seven. doi:10.1159/000443378. PMC4908446. PMID 27386457.
- ^ "B-Complex Vitamins: Benefits, Side Effects and Dosage". Healthline. 2018-06-07. Retrieved 2021-06-21 .
- ^ Floersheim, GL (1989). "Behandlung brüchiger Fingernägel mit Biotin" [Handling of brittle fingernails with biotin]. Zeitschrift fur Hautkrankheiten (in German). 64 (one): 41–eight. PMID 2648686. INIST:7283755.
- ^ Hochman, LG; Scher, RK; Meyerson, MS (April 1993). "Brittle nails: response to daily biotin supplementation". Cutis. 51 (4): 303–305. PMID 8477615. INIST:4679255.
- ^ Langan, Robert C.; Zawistoski, Kimberly J. (xv June 2011). "Update on Vitamin B12 Deficiency". American Family Physician. 83 (12): 1425–1430. PMID 21671542.
- ^ "17 Science-Based Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids". Healthline. 2018-ten-fifteen. Retrieved 2021-06-21 .
- ^ Szyszkowska, Barbara; Łepecka-Klusek, Celina; Kozłowicz, Katarzyna; Jazienicka, Iwona; Krasowska, Dorota (June 2014). "The influence of selected ingredients of dietary supplements on skin condition". Advances in Dermatology and Allergology/Postȩpy Dermatologii i Alergologii. 31 (iii): 174–181. doi:10.5114/pdia.2014.40919. PMC4112259. PMID 25097490.
- ^ Zempleni, J; R.B. Rucker; D.B. McCormick; J.W. Suttie (2007). Handbook of vitamins (fourth ed.). [ folio needed ]
- ^ "How to Increase the Absorption of Atomic number 26 From Foods". Healthline. 2017-06-03. Retrieved 2021-06-21 .
- ^ Singal, Archana; Arora, Rahul (2015). "Nail as a window of systemic diseases". Indian Dermatology Online Journal. half dozen (ii): 67–74. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.153002. PMC4375768. PMID 25821724.
- ^ "- Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D - NCBI Bookshelf". 2011.
- ^ Cashman MW, Sloan SB (2010). "Nutrition and nail disease". Clinics in Dermatology. 28 (iv): 420–25. doi:x.1016/j.clindermatol.2010.03.037. PMID 20620759.
- ^ "Surreptitious Ingredient: Acrylic Liquid".
- ^ Laneri, Raquel (18 April 2017). "Muslim women are showing off their insane nail fine art in 'nelfies'". NY Mail . Retrieved 21 February 2019.
- ^ "Gel Manicures Look Adept, merely What'due south the Damage to Your Nails?". 12 Oct 2019.
- ^ "Fiberglass".
- ^ "Everything You Need to Know Almost Dip Pulverisation Nails". 3 January 2017.
- ^ Simms, Janet (2003). A Practical Guide to Beauty Therapy for NVQ Level 2. ISBN9780748771509.
- ^ "How to Remove Dip Nails at Dwelling". fourteen April 2020.
- ^ "Crash breaks adult female's tape-length fingernails". NBCNews. December 2009.
- ^ a b Ankel-Simons, Friderun (8 January 2007). Primate Beefcake: An introduction (3rd ed.). London, UK: Bookish Printing. pp. 342–344. ISBN978-0-12-372576-ix.
- ^ Maiolino, S.; Boyer, D.Thousand.; Rosenberger, A. (2011). "Morphological correlates of the preparation claw in distal phalanges of platyrrhines and other primates: A preliminary study". The Anatomical Record. 294 (12): 1975–1990. doi:10.1002/ar.21498. PMID 22042603. S2CID 3939930.
- ^ Hamrick, Mark Due west. (1998). "Functional and adaptive significance of primate pads and claws: Bear witness from New Earth anthropoids". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. Wiley-Liss. 106 (2): 113–27. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-8644(199806)106:2<113::AID-AJPA2>3.0.CO;2-R. PMID 9637179.
External links [edit]
-
 Media related to Nails at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Nails at Wikimedia Commons
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nail_%28anatomy%29
Posted by: stubbsshouthat1940.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is The Skin Under Fingernails"
Post a Comment